Research Smart Software Business
The increasing importance of digitization represents above all Classic industries, in which products and services with a relatively small software component were formerly an object of value creation, under enormous competitive pressure. Classic industries are forced to realign their existing business areas in order to remain competitive against emerging companies with software-intensive products. This realignment often leads to digitalization of the existing product and service portfolio or even the development of entirely new services. Companies are often faced with the challenge of aligning their business models to create value through software-intensive products within cooperative value creation networks.
Software-intensive products are understood as multidisciplinary products or hybrid service bundles, whereby the software component has a decisive relevance in its added value. Multidisciplinarity implies a convergence of disciplines previously treated separately, which differ significantly in their characteristics. The resulting complexity is sometimes reflected in the product development of software-intensive products. For example, software products differ significantly from physical products in their development cycles. Accordingly, agile process models (e.g. Scrum) are often used in software development, while the development of physical products usually. takes place under plan-driven process models (e.g. V-model).
The product development of software-intensive products requires the integration of plan-driven process models with agile process models. It is necessary to create a common understanding of the requirements across the individual disciplines. The aim of the research project is to develop a process model for the product development of software-intensive products by integrating agile with plan-driven process models with a focus on relevant techniques of requirements engineering.
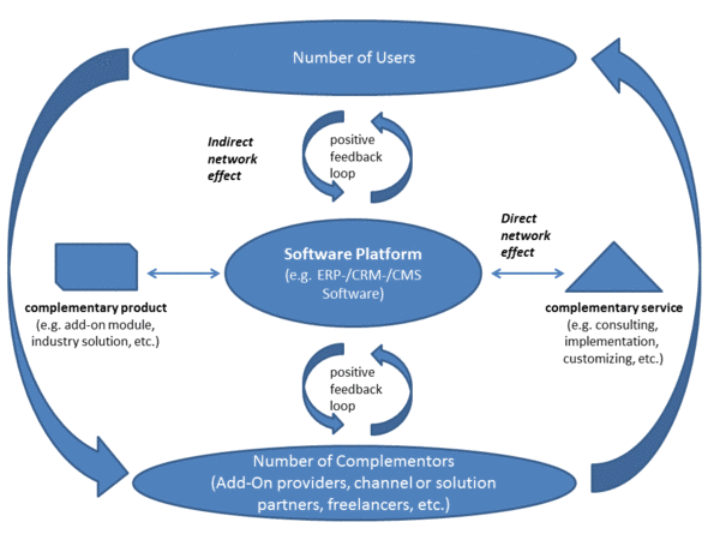
As part of the socio-economic and technology-induced changes in industry and society, which are summarized in everyday language under the keyword "digitization", companies in traditional sectors such as mechanical engineering, but also in the IT sector, are put under considerable pressure to change. Business models that deal with the development and sale of monolithic products are increasingly being replaced by so-called hybrid service packages. Complex ecosystems emerge from (software) platforms and corresponding complementary offers.
At the same time, companies are forced to significantly reduce the speed of development and to convert new technologies into marketable products as quickly as possible.
Subproject
Technology driven Quality Function Deployment
Since the 1960s, QFD has been used for method-based improvements in the technical and relative quality of existing products. The project examines the extent to which the logic inherent in QFD can also be applied to the method-based analysis of new technologies for the achievable relative quality in customer segments that have yet to be defined. The goal is therefore the conception and evaluation of a methodical approach to analyze the potential of new technologies for the development of networked, software-intensive products based on QFD according to ISO 16355 ("Application of statistical and related methods to new technology and product development process").
Problem
After a "wave of quality" in the 90s through TQM, ISO 9000, CMMI and other approaches, the focus in recent years has been on innovative and agile approaches such as Scrum and Design Thinking in software development. However, the ongoing digitalization and high importance of IT for all industries currently require a rethink: With software-intensive concepts such as Industry 4.0 and autonomous driving, defects in software quality pose not only high risks for business success, but also for health and safety.
Aim
The aim of the project is to analyze the state of research and practice in the field of software quality management. Subsequently, an assessment is to be made of the extent to which the existing approaches meet the software quality requirements of agile and digital business fields. In terms of method, instruments such as structured literature analysis, web research (seminars, products, services, software etc.) and trend analysis (e.g. using Google Trend) are used.
As part of the research project Individualization of Business Software in the Context of Organizational Networks (INDUS.NET), empirically validated recommendations are to be developed based on the success factors to be identified, which companies can serve in practice as a frame of reference for the effective and efficient design of the customization of business software. A contingency approach is followed, i.e. Depending on the situation (e.g. size of the provider, type of business model being pursued, type of software offered or type of organizational network), differentiated recommendations should be made for the different actors in the area of business software. The special circumstance of erosion of corporate structures and increasing networking (e.g. through software ecosystems, software platforms or open innovation) is given special consideration.
Research Sustainable Mobility
The focus of the EGemi research project is on the generation and integration of real-time data for line-based „Bürgerbusse“, flexible „Bürgerrufatos“ as well as rideshare services in electronic journey planner systems. Building on the results of the FEeoV preliminary study, funded in the mFund funding line, the merging and further development of the mobility solutions of the project partner Match Rider UG and the associated partner SIVIS GmbH will create a central administration tool with which the booking process and the scheduling of trips for „Bürgerbusverkehre“, „Bürgerrufautoverkehre“ and rideshare can be handled.
It is of interest to what extent information technology solutions can support services of general interest in rural areas. In addition to objectively measurable variables such as punctuality of the connections and connecting journeys achieved, it can be assumed that trust in the modes of transport is a decisive factor for the acceptance of multimodal travel chains, including voluntary community traffic among users. For a closer examination of the confidence-building criteria, a comprehensive analysis of all the stakeholders involved is first necessary: based on this, an analysis of the specific needs of the stakeholders for multimodal community traffic in general and in particular with regard to the software solution to be developed is carried out in accordance with the procedure model of ISO 16355. On the one hand, this is done in order to generate a common understanding of the problem for all project participants, and to determine specific requirements for the software solution. Further scientific questions concern the evaluation of the relative and technical quality of the solution developed in the project by the stakeholders, as well as the social added value of the project to be achieved overall.
Problem:
Real-time information is becoming increasingly important to enable intermodal travel chains and has already been implemented in urban areas for public transport. As an app-based electronic timetable information system for passengers, the basis has been created to make public transport attractive. In rural areas, the spread of „Fahrgastinformatonssystemen“ (passenger information systems) has not progressed as far. Voluntary community traffic is widespread here, which cannot meet the often cost-intensive technical requirements for a connection to passenger information systems.
Goal:
The aim of the project is to generate and integrate timetable and real-time data for voluntary organised mobility offers in dynamic information systems. A new usage and networking concept for the feasibility of intermodal travel chains in rural areas is being implemented, taking into account line-based community transport („Bürgerbusse“). This creates predictable and consistent travel routes that offer great added value for passengers when it comes to securing connections.
Expected Results:
The integration of voluntary mobility offers into a software ecosystem using the example of Baden-Württemberg takes place using the “MatchRiderGO” app via the existing interfaces of the Nahverkehrsgesellschaft Baden-Württemberg mbH. In a first stage of expansion, the integration of timetable data from „Bürgerbusse“ transport into a regional data hub and the display in an app for the passengers will be implemented. The generated schedule data is provided as open data by the mCLOUD.
Consortium:
- University of Stuttgart, Department VIII - Information Systems II
- Nahverkehrsgesellschaft Baden-Württemberg (NVBW)
- Match Rider UG
- Federal Ministry of Transport and Digital Infrastructure
Runtime:
January – December 2019
Consortium:
- S3 Innovations
- Electrify-BW e.V.
- University of Stuttgart, Department VIII - Information Systems II
- Stuttgart Media University
Consortium:
- University of Stuttgart, Department VIII - Information Systems II
- Nahverkehrsgesellschaft Baden-Württemberg (NVBW)
In the spirit of the share economy, the project should promote a rethinking of society that increases people's willingness to share their cars. In the future, the applicants would like to implement a functioning network of dynamic carpools, even on short and medium distances.
Consortium/Project partners
- Match Rider UG
- University of Stuttgart, Department VIII - Information Systems II
- Ministry of Science, Research and Art Baden-Württemberg
- CyberForum e.V.
The aim of the "Apricot" project is to develop an appliance, i.e. a pre-installed, pre-configured and immediately usable IT device. Through the use of the appliance and the accompanying software components and services also developed as part of the project, SMEs in the area of mobility and complementary services can network easily, cost-effectively and securely (so-called co-competition network) and jointly offer higher-quality service packages that have international exemplary character and simplify the use of environmentally friendly mobility services.
Consortium / Project Partner
- University of Stuttgart, Department VIII - Information Systems II
- Federal Ministry of Education and Research
- highQ Computerlösungen GmbH
Founding of a voluntary citizens‘ mobility association that supplements local public transport with a large e-car
Project partners
- Ministry of Rural Areas and Consumer Protection Baden-Württemberg
- City Boxberg
- Institute for Railway and Transport Science at the University of Stuttgart
Project duration
May 2013 – December 2015
Two public bus routes in the Bad Boll area are intended to supplement the public transport services geared towards the city of Göppingen through the use of electrically operated public buses. In order to guarantee the connection to existing public transport offers, dynamic driver and passenger information should be set up at the connection stops and the „Bürgerbus“ lines connected to the central data hub of Baden-Württemberg, so that an innovative, integrated and sustainable mobility concept is created.
Project partners
- Association region Stuttgart - corporation under public law
- Wirtschaftsförderung Region Stuttgart GmbH
- Local administration area Bad Boll
- VWI Verkehrswissenschaftsliches Institut Stuttgart GmbH
- highQ Computerlösungen GmbH
Project duration
January 2013 – December 2015
The aim of the e-Bürgerbus-Wiki project is to promote the exchange of knowledge, especially in Baden-Württemberg, on the subject of electrically powered „Bürgerbusse“ by implementing a wiki and to create a knowledge base that is up-to-date at all times, with the help of which existing and founding „Bürgerbussvereine“ use their scarce resources can use more efficiently.
Project Partners
- e-mobil BW - Landesagentur für Elektromobilität und Brennstoffzellentechnologie Baden-Württemberg GmbH
Project duration
Since November 2012
Research Advanced Manufacturing
Problem and Target
The Internet of Things offers manufacturing companies in machine tool manufacturing great potential for additional income. Networking and corresponding software enable the machine tools to be modularly equipped with additional smart and value-adding services.
Such digital services are provided via digital platforms, which in practice are also referred to as industrial IoT (iIoT) platforms.
As a concept, platforms already play a central role in many domains such as mobile devices, smart homes or connected automobiles. Nevertheless, platform-based business models for manufacturing companies in the industrial context have not yet been researched.
In addition, platforms are a central component of flexible value creation networks, whereby the platform providers can often play a focal role and design the platform.
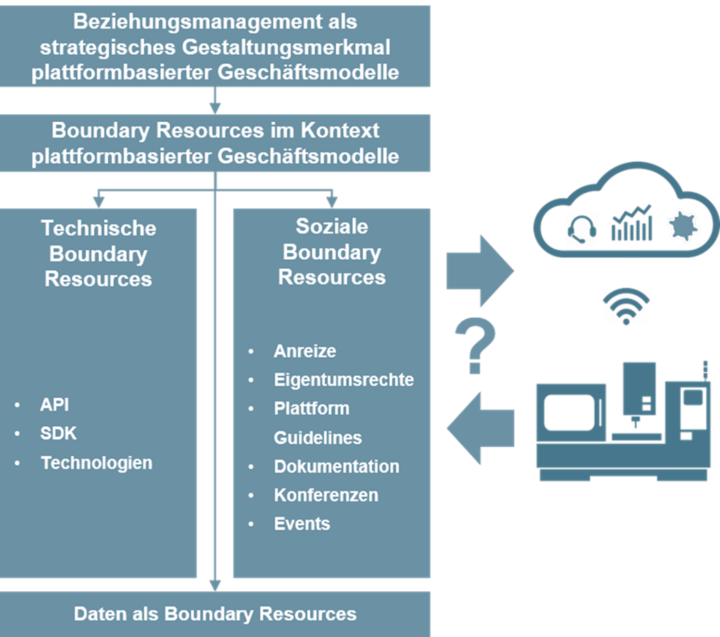
Strategic relationship management, as a design feature of platform-based business models, offers manufacturing companies the opportunity to manage and control the complementary third-party providers (e.g. services and software products). Relationship management thus represents an attractive and interdisciplinary field of research.
Walkthrough
The research project examines the boundary resources approach as a design feature of relationship management for platform providers in the context of the industrial Internet of Things.
Boundary resources can be understood as different resources that give partners access to the platform and their core technologies and enable them to use the technical functions of a platform.
Planned procedure for the research project:
- Platform definition and adaptation of the platform and ecosystem concept for mechanical engineering
- Evaluation of the current state of the art in the use of boundary resources on iIoT platforms
- Investigation of quality factors in the identified boundary resources and their influence on the growth of iIoT ecosystems
- Derivation of recommendations for providers of ioT platforms for stakeholder-centered design of boundary resources to gain value creation partners
Problem and Target
Cloud Manufacturing transfers the principles of cloud computing to the production landscape. The high-level idea is the interaction of the integration of distributed resources (production resources or production skills) and the distribution of these integrated resources via a cloud platform.
It has been identified in the literature that the topic of information security and trust in this new production paradigm have so far been insufficiently examined.
While the trust situation already plays a significant role in classic cloud computing, it is fundamentally tightened in cloud manufacturing, since the holistic production process is carried out via a cloud.
In addition to information and data, there are for example, company secrets and special knowledge about production "in the cloud" - these can even lead to loss of competitive positions and competitiveness if misused or incorrectly handled. Accordingly, this situation is also characterized by a high degree of uncertainty and vulnerability to users.
Walkthrough
The goal of the research project is to determine significant influencing factors from the user perspective, which have a positive or negative influence on the formation of trust in a cloud manufacturing platform.
After all, these form the basis for deriving design recommendations for providers of cloud manufacturing platforms.
In the previous work, the problem domain of trust in cloud manufacturing could be defined and structured. In addition to the existing research gap, a clear need for investigation was identified, since previous knowledge in thematically related areas cannot be directly transferred.
Consortium
- Compacer GmbH
- University of Stuttgart, Department VIII - Information Systems II
- JURIBO law firm
- HAW Hamburg research group "Blockchains in Sensornetzwerken"
- Materna GmbH
Experience the Internet of Things with the IoT Laboratory at the Chair of Business Administration and Information Systems II
Digitization also plays an important role at WIUS in the current research agenda. The Internet of Things makes it possible to network a wide variety of objects with relatively little effort and the data of these objects, for. B. to receive or even evaluate with mobile devices.
But the users also need suitable applications for this. In order to create such applications and to implement the concepts from research and teaching through prototype applications, the WIUS chair has its own IoT laboratory thanks to the cooperation with the Graduate School of advanced Manufacturing Engineering (GSaME) to support research.
In the following you will find information about what our IoT laboratory consists of and what cooperation options there are.
Equipment of the IoT laboratory with modern devices for development
The equipment of the laboratory includes, for example. mobile devices and desktop devices with current operating systems: Apple iOS, Google Android and Microsoft Windows.
The devices are equipped with appropriate development and test tools. Thus, the chair's IoT laboratory creates a holistic development environment and offers all interested parties the opportunity to program the applications for most of the current operating systems and to implement the concepts developed as a prototype.
Our IoT laboratory has already been used in the past for the prototypical implementation of theoretical concepts from previous dissertations.
In addition, thanks to the IoT Laboratory, some concepts from the lecture in our chair can be digitized as applications (House of Quality, compass for the management of IT products).
Ergonomie messen mit der Eyetracking Brille als Bestandteil des IoT Labors
The eyetracking glasses Tobii Pro are also part of the equipment portfolio of the IoT laboratory at the chair. Interested parties have the opportunity to test the prototypes with regard to their design or ergonomics and to record and measure the results.
In this way, technical innovations can also be researched from a user or customer perspective. In the past, the glasses were also used for different student theses.
Opportunities for cooperation
We enable the use of the IoT laboratory both in the form of research collaborations with partners from research and industry, as well as for student theses. If you are interested or have any other questions about the IoT laboratory, please contact Dimitri Petrik.
The aim of the project is to develop a metamodel for modeling processes in all domains in manufacturing companies and to develop a prototype of a suitable modeling tool.
Consortium/Project partners:
- University of Stuttgart, Department VIII - Information Systems II
- German Research Foundation
- Graduate School of Excellence advanced Manufacturing Engineering (GSaME)
- University of Stuttgart, Institute for Architecture of Application Systems
The research area IT integration of distributed value networks deals with the integration of data, applications and business processes. Possibilities for the integration of (sub) functions in company-specific and cross-company applications are examined.
Integration approaches are examined from a technical as well as a business-organizational perspective. The degree of integration should be made measurable using suitable approaches.
In connection with the features to be evaluated for the characterization of integration objects, statements about optimal degrees of integration should be made possible.
The research area also focuses on cost-benefit analyzes in order to investigate the cost-effectiveness of IT integration in distributed value creation networks. The quality assurance of IT integration as well as the project management with regard to the IT integration of distributed value creation networks are also in the focus of attention.
Consortium/Project partners:
- University of Stuttgart, Department VIII - Information Systems II
- German Research Foundation
- Graduate School of Excellence advanced Manufacturing Engineering (GSaME)
- University of Stuttgart, Institute for Architecture of Application Systems